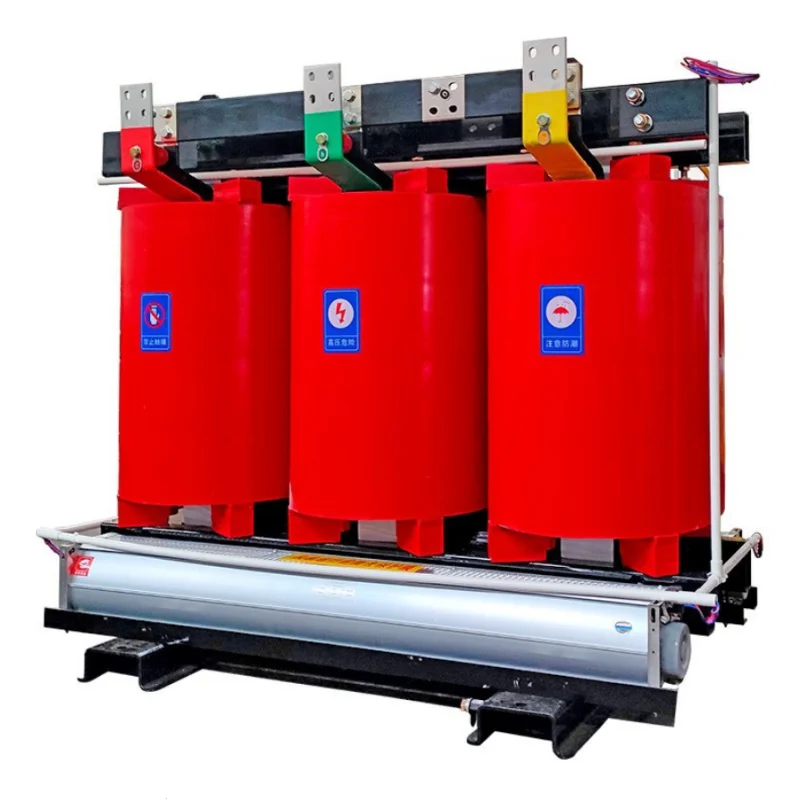
When it comes to power distribution in industrial and commercial environments, dry type transformer cores play a crucial role. Unlike oil-filled units, dry type transformers use air as the cooling medium, making them safer, cleaner, and more sustainable. But how exactly does the transformer core impact performance, efficiency, and cost over the equipment’s lifecycle? Let’s break it down.
What Is a Dry Type Transformer Core?
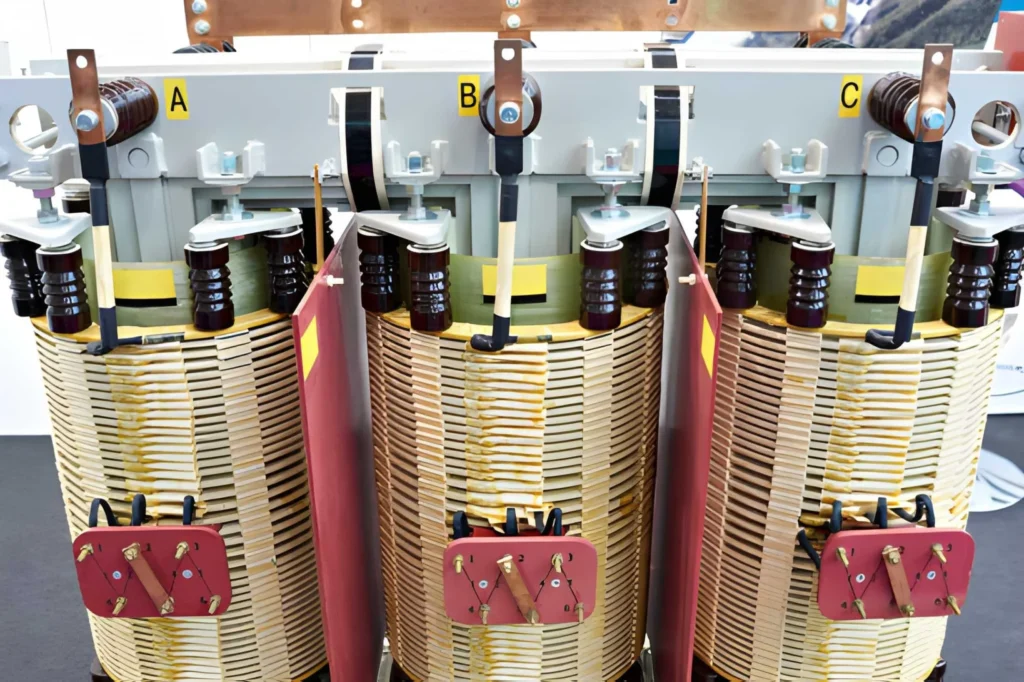
At its heart, a dry type transformer relies on magnetic induction. The core, made of laminated electrical steel or amorphous alloy, channels magnetic flux efficiently between primary and secondary windings. By design, the core determines how much energy is lost as heat, how much noise is generated, and how much space the unit occupies.
The core material—whether CRGO (Cold Rolled Grain Oriented steel) or amorphous metal—is what sets one transformer apart from another. For projects demanding high efficiency and low operating costs, choosing the right core is not just a technical decision—it’s a business one.
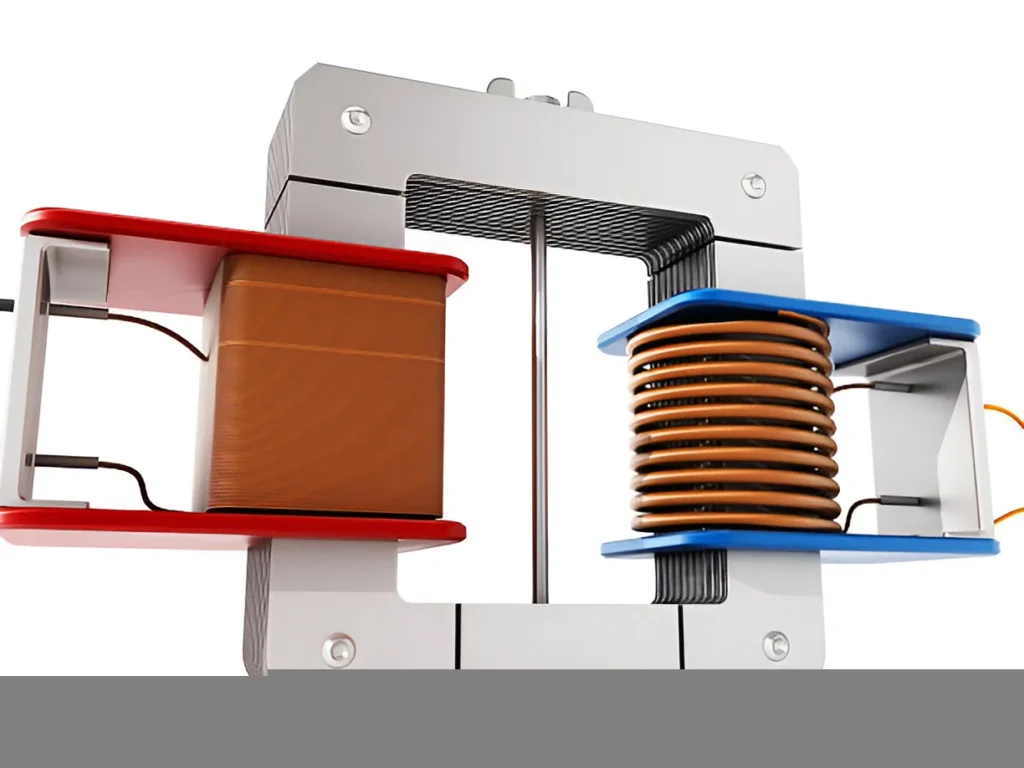
Why Core Design Matters in Industrial Applications
A dry type transformer’s core influences efficiency, safety, and longevity. For purchasing managers, EPC contractors, and electrical engineers, those three words mean everything.
- Efficiency: The better the magnetic permeability of the core, the lower the no-load losses. That translates into long-term energy savings.
- Safety: Since there’s no oil, the risk of fire or environmental contamination is minimal—crucial for hospitals, data centers, and public buildings.
- Longevity: A well-designed core runs cooler, reducing insulation stress and extending service life.
Many modern manufacturers now offer cast resin transformer cores and vacuum pressure impregnated (VPI) cores, which provide enhanced protection against moisture, corrosion, and dust.
Common Core Materials and Their Characteristics
Different applications call for different core materials. Here’s a comparison:
| Core Material | Composition | Efficiency Level | Typical Use Cases | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRGO Steel | Silicon steel with grain orientation | High | Industrial LV/MV transformers | Moderate |
| Amorphous Alloy | Non-crystalline metal ribbons | Very high | Energy-saving systems, Green buildings | High |
| Ferrite | Ceramic magnetic material | Medium | Compact transformers, electronics | Low |
While CRGO cores remain the industry standard due to balanced performance and cost, amorphous core dry type transformers are gaining traction. They offer up to 70% lower no-load losses—an attractive feature for enterprises seeking to meet ISO 50001 or green energy compliance.
Types of Dry Type Transformer Core Constructions
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to core design. The construction determines how efficiently the core handles magnetic flux and mechanical stress.
- Core Type – The windings surround the core legs. Most common for large power and distribution transformers.
- Shell Type – The core surrounds most of the windings, providing better short-circuit strength.
- Toroidal Core – Circular shape offering low electromagnetic interference and minimal losses—often used in compact HVAC or rail systems.
Each type serves different priorities: high current capacity, compact size, or advanced noise reduction.
Design Innovations and Manufacturing Process
A modern dry type transformer core is more than just steel and copper. It’s a product of advanced magnetic modeling, laser cutting technology, and precision assembly.
- Step-lap core construction reduces joint losses and noise.
- Epoxy resin cast insulation systems enhance mechanical durability.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) helps engineers design for optimal heat dissipation.
Manufacturers that specialize in dry type transformers often verify every stage—from core cutting to vacuum drying—to ensure consistent magnetic performance. For B2B buyers, working with suppliers that can provide test certificates (like IEC 60076 compliance) ensures your investment meets both performance and quality expectations.
Energy Efficiency and ROI Considerations
Energy efficiency is no longer just a buzzword; it’s a procurement requirement. When selecting a dry type transformer core, consider total ownership costs (TOC) instead of upfront prices.
- No-load losses (core losses) can account for over 25% of total transformer losses.
- A small percentage gain in efficiency may save thousands in electricity bills annually for continuous operations.
- Amorphous metal cores often pay back their premium cost in 3–5 years through energy savings.
Here’s a simplified ROI comparison:
| Specification | CRGO Core | Amorphous Core |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Moderate | High |
| No-Load Loss | 100% (base) | 30% lower |
| Operating Noise | Medium | Low |
| ROI Period | 5–6 years | 3–4 years |
When scaling a plant or upgrading an existing network, the transformer core choice is a long-term performance lever.
Application Sectors and Use Cases
Dry type transformers equipped with efficient cores are widely used across sectors that prioritize safety, reliability, and environmental compliance:
- Hospitals – Low-fire-risk installations near patient areas.
- Data Centers – Clean operation with low harmonic interference.
- High-Rise Buildings – Compact, air-cooled systems that save space.
- Renewable Energy Plants – Rugged designs supporting solar and wind grids.
- Oil & Gas Facilities – Explosion-proof cast resin cores in hazardous zones.
OEMs and system integrators often specify custom transformer cores for these installations, ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure and local safety standards.
Procurement Tips for B2B Buyers
If you are sourcing dry type transformer cores for a new project, here’s what to evaluate before sending an inquiry:
- Core Material Origin – Verify if it’s CRGO or amorphous steel from reputable suppliers (like Nippon Steel or AK Steel).
- Compliance Standards – Look for IEC, ANSI/IEEE, or ISO certifications.
- Thermal Class – Ensure the transformer’s insulation matches your ambient conditions (e.g., Class F or H).
- Warranty and Service – A 5–10-year warranty demonstrates confidence in core design.
- Customization – Specify dimensions, voltage ratings, and environmental conditions for accurate quoting.
Ready to find a reliable dry type transformer core manufacturer? Contact our technical sales team today for a quote or engineering consultation.
Emerging Trends in Transformer Core Technology
With sustainability goals rising, R&D efforts are focusing on:
- Nanocrystalline core materials that push efficiency boundaries even further.
- 3D lamination simulations to reduce residual magnetism.
- AI-based performance diagnostics integrated into smart transformers.
Such innovations are reshaping how power equipment is designed and maintained, giving facility owners better insights into energy use and preventive maintenance.
Selecting the right dry type transformer core is more than a technical checklist—it’s a smart investment decision. From material to design and manufacturing precision, each factor influences your system’s efficiency, reliability, and safety.
Whether you’re an engineering contractor, procurement manager, or system designer, optimizing your transformer’s core can yield measurable cost reductions and sustainability gains.
If you’re evaluating core designs or need expert advice, reach out to our engineering team—we’ll help you choose the ideal core solution to power your next project efficiently.
FAQ
What’s the main advantage of a dry type transformer core over oil-filled designs?
A dry type unit eliminates fire hazards and oil leaks, offering lower maintenance and safer indoor installation.
How long does a dry type transformer last?
Typically 25–30 years, depending on core material quality and operating environment.
Are amorphous core transformers worth the extra cost?
Yes, especially for facilities operating 24/7. The energy savings offset the initial investment.
Can transformer cores be customized for OEM applications?
Absolutely. Core geometry, insulation, and winding configuration can be tailored for project specifications.