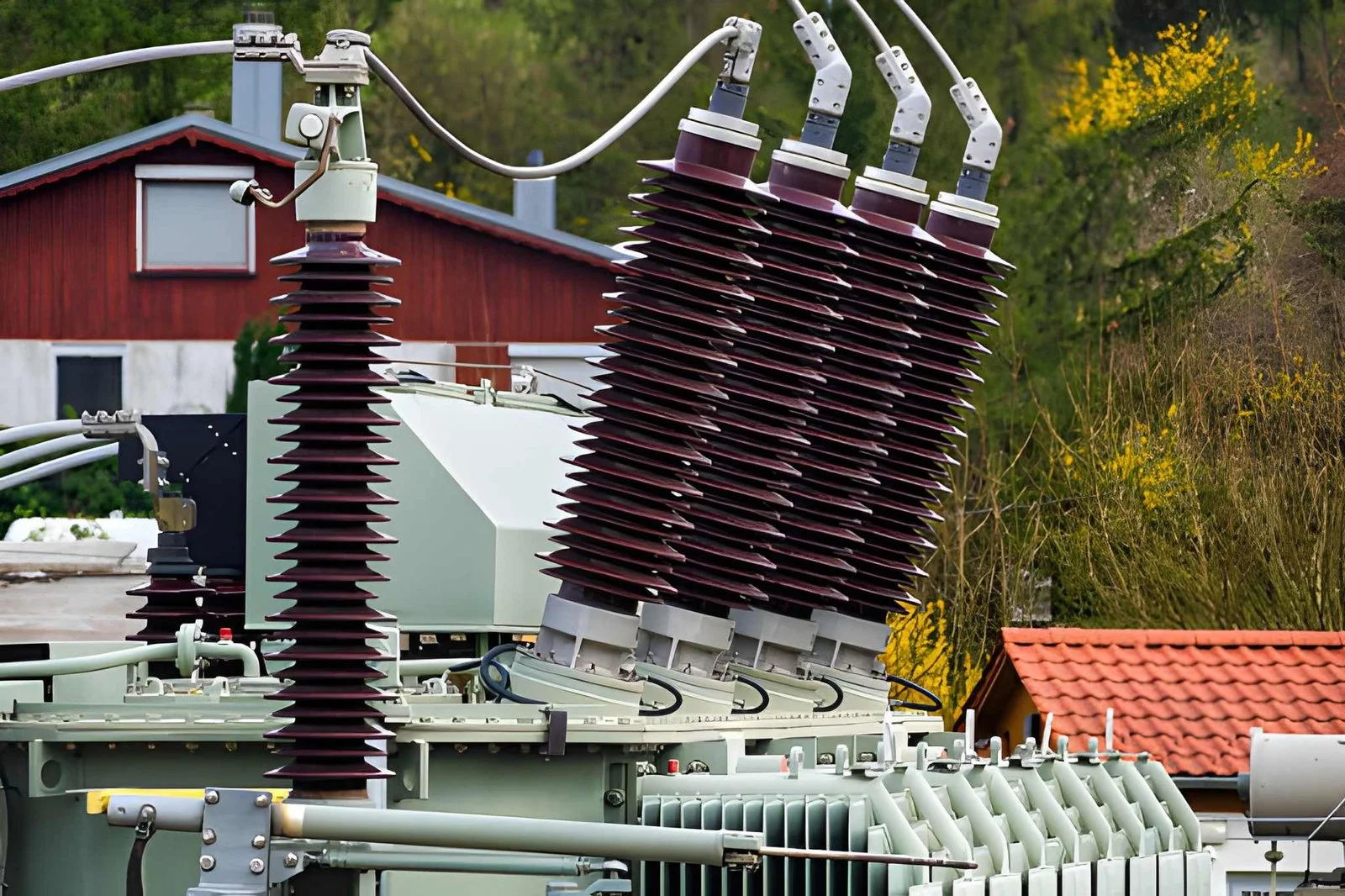
What Is a Dry-Type Transformer?
A dry-type transformer is a type of electrical transformer that uses air as its primary cooling and insulating medium instead of oil or other liquid dielectrics. This core principle of air-cooled insulation makes dry-type transformers safer, more environmentally friendly, and better suited for indoor use where fire hazards from oil leaks must be minimized.
Basic Construction
Dry-type transformers consist of key components:
- Core: Usually laminated steel to reduce energy losses.
- Windings: Copper or aluminum coils wrapped around the core.
- Enclosures: Protective cabinets that support ventilation and protect against dust or moisture.
- Cooling Methods: These typically include natural air cooling (self-ventilated) or forced air cooling using fans to increase heat dissipation.
Unlike oil-immersed transformers, dry-type versions avoid liquid dielectric fluids. Instead, they rely on air to carry heat away from windings and core components.
Historical Evolution and Growing Adoption
Originally, dry-type transformers were limited to lower power ranges due to cooling constraints. However, advances such as vacuum pressure impregnation (VPI) and cast resin insulation have improved their mechanical strength and thermal stability. These innovations have expanded their use beyond sensitive indoor environments (like hospitals and data centers) to commercial and heavy industrial installations.
Today, dry-type transformers are increasingly popular for their safety, reliability, and environmental benefits. Their fire-resistant, low-maintenance design makes them ideal for settings where oil spills or explosions are unacceptable risks.
In , dry-type transformers combine robust core and winding design with air-cooling technology to deliver safe, efficient power distribution in a variety of demanding applications—all without the risks tied to liquid cooling fluids.

Main Types of Dry-Type Transformers
Dry-type transformers come mainly in a few key types, each suited to different needs and environments.
Vacuum Pressure Impregnated (VPI) Transformers
VPI transformers are built by impregnating the transformer windings with insulating varnish under vacuum and pressure. This process creates strong, moisture-resistant insulation, improving mechanical strength and thermal stability. VPI dry type transformers typically handle medium voltage applications and are known for reliable performance in demanding conditions. Their robust insulation makes them great for locations where humidity and vibration might be a concern.
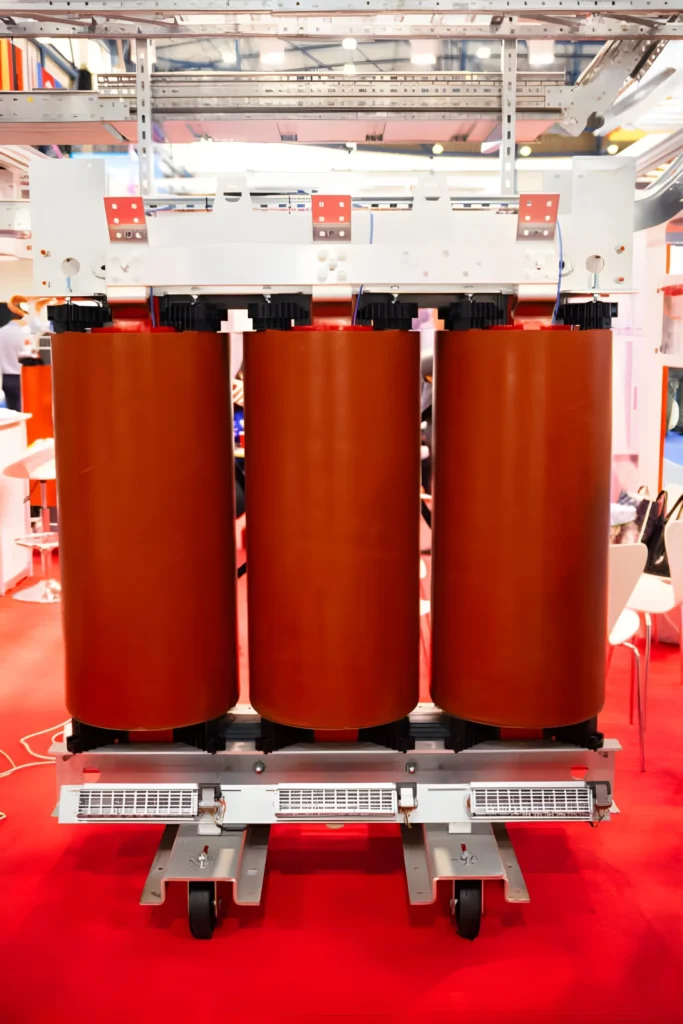
Cast Resin Transformers (CRT)
Cast resin transformers use epoxy resin to encapsulate the windings completely, providing excellent fire resistance and protection against moisture, dust, and chemicals. The epoxy resin transformer design is compact and often chosen for indoor power transformers where space and safety are critical. Cast resin transformers feature high overload capacity and meet tough environmental and safety certifications like F1 fire class and E2 environmental class. These traits make CRTs especially popular in commercial and industrial settings.
Other Specialized Variants
- Ventilated Dry-Type Transformers: Also known as open wound types, they allow natural air circulation around the coils, suitable where cooling access is possible.
- Encapsulated (Potted) Transformers: These are fully sealed with resin, providing extra protection against contaminants and moisture.
- Totally Enclosed Non-Ventilated (TENV) Transformers: Designed for harsh or contaminated environments where dust, dirt, or corrosive elements are present, TENV units offer maximum protection with no ventilation openings.
Each of these dry-type transformer types balances insulation method, cooling style, and protection to match specific operational needs.
For detailed insights on dry-type transformer insulation and core design, you can refer to our guide on dry-type transformer core technology and applications.
Dry-Type vs. Oil-Immersed Transformers: A Detailed Comparison
When choosing between dry-type transformers and oil-immersed transformers, understanding their core differences helps in making the right decision for your project.
Cooling and Insulation
| Feature | Dry-Type Transformer | Oil-Immersed Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Air-cooled (natural or forced air) | Oil acts as coolant and insulator |
| Insulation | Solid insulation: epoxy resin, VPI | Liquid dielectric (mineral or synthetic oil) |
Dry-type transformers rely on air for cooling and use solid insulation materials like epoxy resin or vacuum pressure impregnated (VPI) coatings. In contrast, oil-immersed transformers are cooled and insulated by transformer oil, which requires regular maintenance.
Performance Factors
| Factor | Dry-Type Transformer | Oil-Immersed Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Slightly lower due to air cooling | Generally higher efficiency |
| Overload Handling | Limited overload tolerance | Better overload performance |
| Temperature Rise | Higher temperature rise, needs ventilation | Lower temperature rise due to oil |
Dry transformers often handle moderate loads and operate well under controlled environments, but are less tolerant to overloads compared to oil types. They typically run hotter, so ventilation is crucial.
Safety and Environmental Impact
- Dry-Type Transformers pose no risk of oil leaks or fires, making them safer for indoor and sensitive locations.
- Oil-Immersed Transformers carry a risk of oil spills and fire hazards, requiring additional safety measures.
- Environmentally, dry types are more eco-friendly due to no oil use and easier disposal.
Installation and Space Requirements
- Dry-type transformers are compact, lightweight, and ideal for indoor use with minimal space.
- Oil transformers are larger and need containment areas to handle potential oil leaks.
Cost Considerations
| Cost Aspect | Dry-Type Transformer | Oil-Immersed Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Lifecycle Cost | Lower maintenance, longer life | Higher maintenance and oil testing costs |
While dry-type transformers have a higher initial price, their minimal maintenance and safer operation often reduce total lifecycle costs.
For a detailed example of high-quality dry transformers, consider JDZ(8-10R) single-phase fully casted insulation voltage transformer with fuse, offering reliable air-insulated power options for various settings.
Table: Dry-Type vs Oil-Immersed Transformers
| Feature | Dry-Type Transformer | Oil-Immersed Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling | Air (natural/forced) | Oil Immersion |
| Insulation | Solid (epoxy, VPI) | Liquid Dielectric (oil) |
| Overload Capacity | Moderate | High |
| Fire Risk | Minimal | Higher |
| Maintenance | Low | Higher (oil checks, leaks) |
| Installation Space | Compact | Larger |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly | Potential oil contamination |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Lifecycle Cost | Lower | Higher |
This comparison highlights why dry-type transformers are preferred in commercial, industrial, and sensitive environments where safety and sustainability take priority.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dry-Type Transformers
Dry-type transformers offer several clear advantages that make them a popular choice across many sectors. One of the biggest benefits is safety: since they don’t use oil or other liquid dielectrics, there’s no risk of fire or explosion. This makes them ideal for indoor spaces like hospitals, schools, and offices. They also require minimal maintenance compared to oil-immersed transformers, reducing downtime and operational costs. Being eco-friendly and producing less noise during operation adds to their appeal, especially in urban or sensitive environments. Plus, their flexible indoor installation capabilities make them suitable for places with strict fire and environmental regulations.
However, there are some downsides to consider. The initial cost of dry-type transformers can be higher than oil-immersed types, especially for larger capacities. They’re also typically limited in very high-load applications where oil transformers might be more practical. Additionally, dry-type transformers are more sensitive to dust, moisture, and humidity if not housed in proper enclosures, which can affect performance and longevity.
When Dry-Type Transformers Excel
These transformers shine in environments where safety and environmental concerns are top priority. For example:
- Commercial buildings needing fire-resistant, quiet power distribution
- Data centers and industrial facilities where low maintenance and reliability are critical
- Renewable energy setups where oil spills must be avoided
Choosing the right type depends on matching the dry-type transformer’s strengths with your specific project needs, balancing upfront investment with long-term benefits.
For more details on safe and reliable electrical equipment options suitable for indoor environments, explore high-quality vacuum circuit breakers like the VS1-ZN63A Handcart Series, which complement dry-type transformers in modern installations.
Key Applications of Dry-Type Transformers
Dry-type transformers are widely used across various sectors thanks to their safety, reliability, and low maintenance needs. In commercial buildings such as hospitals, schools, offices, and high-rises, they provide dependable power without the fire risks associated with oil-filled models. Their quiet operation and compact design make them ideal for these indoor environments.
In industrial settings like chemical plants, manufacturing facilities, and data centers, dry-type transformers offer superior safety and environmental advantages. Their resistance to dust and moisture (especially in encapsulated or Vacuum Pressure Impregnated (VPI) forms) suits harsh conditions, ensuring consistent performance where failure is not an option.
Renewable energy projects rely heavily on dry-type transformers for wind farms, solar power plants, and other green installations due to their eco-friendly nature and ease of integration. Additionally, marine environments and underground installations benefit from totally enclosed dry-type variants that withstand moisture and contaminants without risking leaks.
Several successful deployments globally demonstrate the versatility of dry-type transformers in meeting stringent safety and performance requirements, making them the go-to transformer choice for sensitive and demanding applications. For more detailed industrial use cases and benefits, you can explore our article on dry type transformers for industrial applications.
How to Select the Right Dry-Type Transformer
Choosing the right dry-type transformer depends on several crucial factors. First, determine your kVA rating and voltage levels to ensure the transformer matches your load requirements accurately. The type of enclosure, often rated by NEMA standards, is vital for protecting the transformer from dust, moisture, and other environmental risks. Consider the temperature rise limits and efficiency standards to optimize performance and energy savings over time.
Understanding your load profile—whether the load is continuous or intermittent—helps in selecting a transformer that can handle occasional overloads without issues. Compliance with international standards like IEC, ANSI, and IEEE ensures safety, reliability, and interoperability of the transformer within your system.
Customization plays a key role, especially for specialized applications or environments requiring unique configurations. Working with a trusted supplier like Kampa allows you to tailor solutions to your project’s exact needs while guaranteeing quality and dependable performance.
For a detailed guide on choosing a dry-type transformer that fits your project perfectly, check out our expert advice on how to select the right dry-type transformers for your project.
Installation, Maintenance, and Best Practices for Dry-Type Transformers
Proper installation and upkeep are key to getting the best performance and longevity from your dry-type transformer.
Site Preparation and Ventilation
- Choose a clean, dry location with enough space for airflow around the transformer.
- Ensure the area is free from dust, chemicals, and excessive moisture to prevent insulation breakdown.
- Ventilation is critical—natural or forced cooling methods should have unobstructed air paths to keep temperatures within design limits.
Routine Inspection and Testing
- Regularly check for dust and debris buildup; clean the transformer exterior and ventilation openings as needed.
- Inspect insulation for signs of wear or damage.
- Perform electrical tests like insulation resistance and winding resistance checks periodically to spot early issues.
- Monitoring temperature rise during operation can prevent overheating problems.
Common Troubleshooting
- Noise: Humming is normal, but loud or unusual sounds may indicate loose components or electrical faults.
- Overheating: Check cooling systems and ventilation; overheating often signals overload or blocked airflow.
- Moisture: Keep an eye out for condensation or dampness that can degrade insulation—using enclosures rated for humid environments helps.
Extending Service Life
- Operate the transformer within its rated capacity and temperature limits.
- Avoid frequent overloads and short cycles to reduce thermal stress on windings and insulation.
- Use a trusted transformer supplier who provides quality products and support, such as Kampa Electric’s range of dry-type transformers, ensuring reliable performance tailored to your needs.
Following these guidelines will help maintain your dry-type transformer’s efficiency, safety, and durability for years to come.